Recent Cases and Guidelines for Pregnant Women to ensure the safety of their unborn babies
Pune, Maharashtra has reported a surge in Zika virus cases, with the Asian strain detected in the city. The virus, first detected in Brazil in 2015, has been spreading rapidly across the globe, and India is no exception. According to recent reports, Pune has reported its third case of Zika virus, with 13 samples sent to the National Institute of Virology (NIV) for testing.
The Zika virus is primarily spread through the bite of an infected Aedes mosquito, which is the same mosquito that transmits dengue and chikungunya. The virus can also be transmitted through sexual contact and from a pregnant woman to her unborn baby. Symptoms of Zika virus infection include fever, rash, and joint pain, which are often mild and may not require hospitalization.
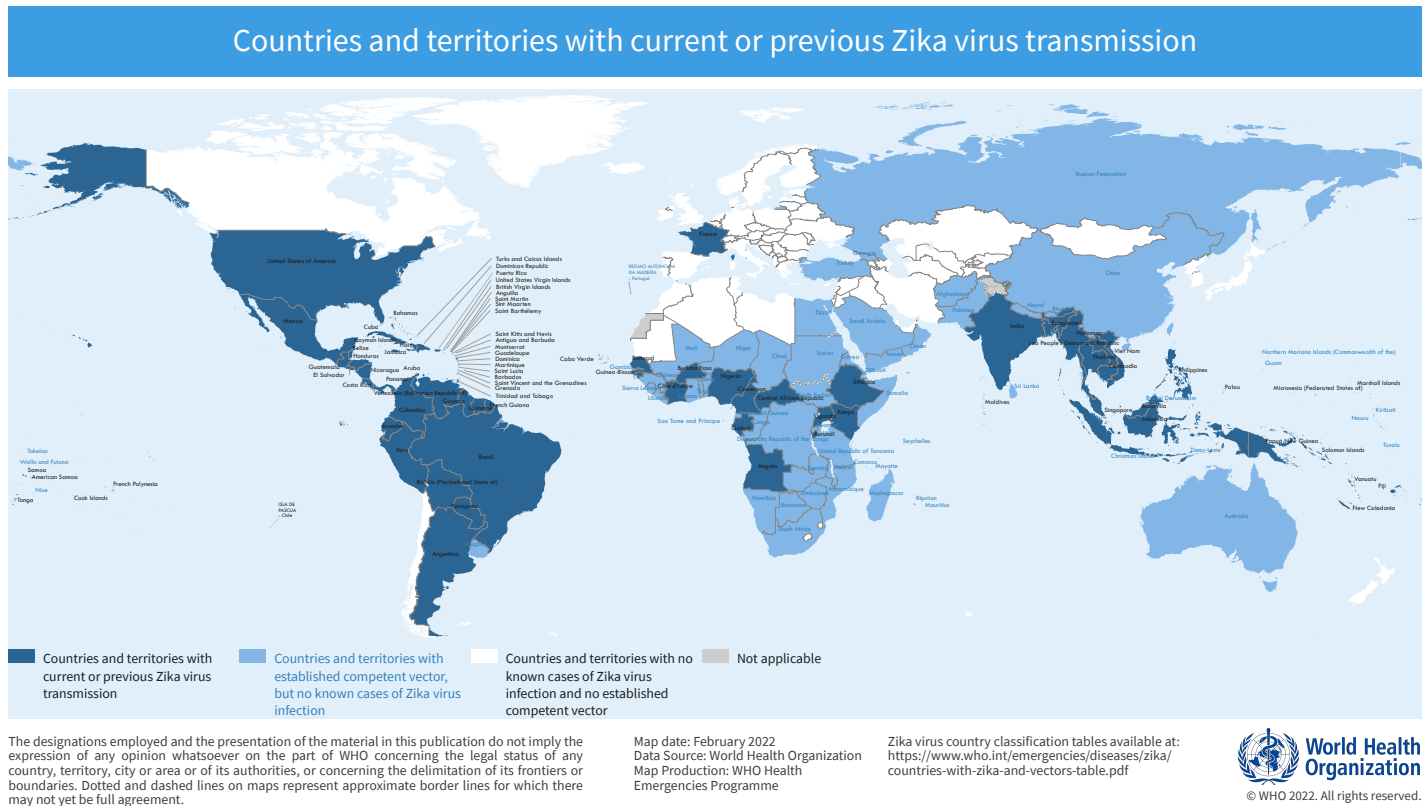
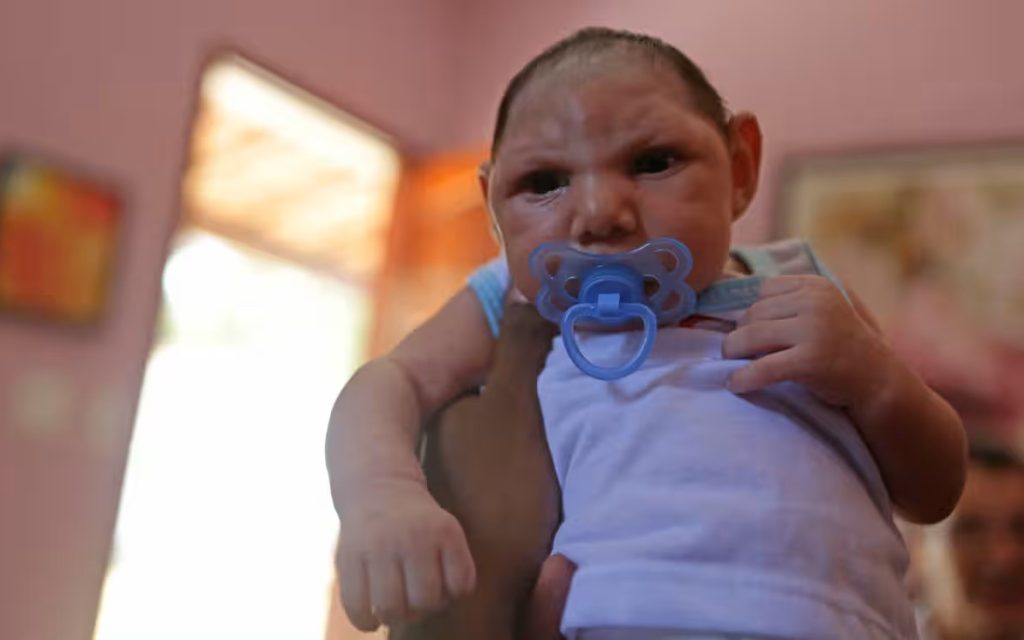
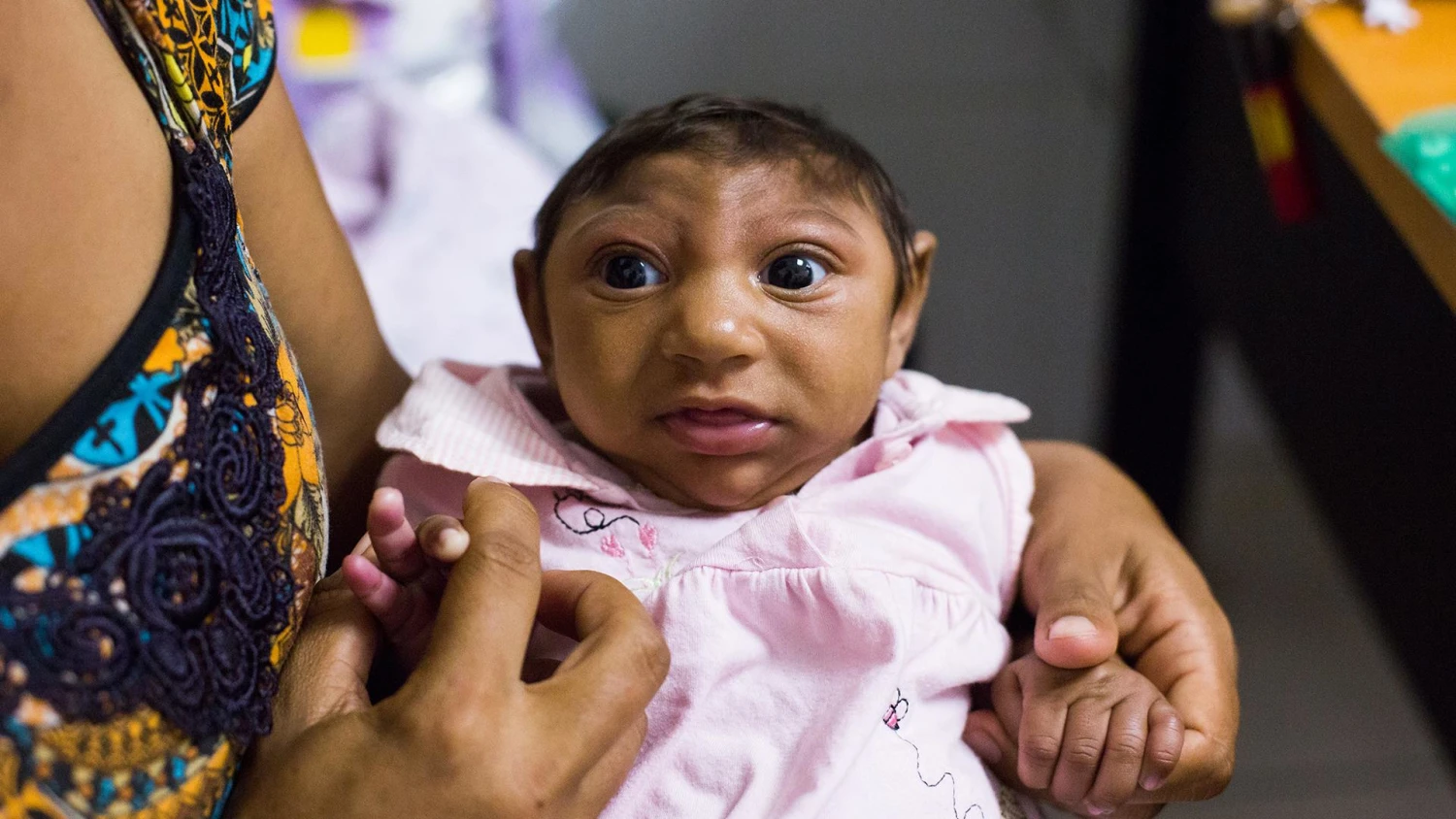
However, the virus can have serious consequences for pregnant women. Zika virus infection during pregnancy has been linked to birth defects, including microcephaly, a condition where the baby’s head is smaller than normal. In severe cases, microcephaly can lead to developmental delays and other neurological problems.
To ensure the safety of pregnant women, new guidelines have been issued by health authorities. These guidelines recommend that pregnant women take precautions to avoid mosquito bites, such as wearing protective clothing, applying insect repellents, and eliminating standing water around their homes. Women who are planning to become pregnant are also advised to take these precautions to reduce the risk of infection.
In addition to these guidelines, health authorities are also working to increase awareness about the Zika virus and its symptoms. This includes conducting public awareness campaigns and educating healthcare providers about the virus.
In conclusion, the Zika virus is a growing concern in Pune, Maharashtra, and it is essential that pregnant women take precautions to avoid infection. By following the new guidelines and taking steps to prevent mosquito bites, women can reduce their risk of infection and ensure the health and well-being of their unborn babies.


 By
By

















