Understanding Mpox and Its Emerging Threats
Mpox, formerly known as Monkeypox, is a zoonotic disease caused by the Mpox virus, closely related to the variola virus responsible for smallpox. The disease has historically been endemic to parts of Central and West Africa, but recent global outbreaks have highlighted its potential as a significant public health concern. With the discovery of a new strain in China, the stakes are higher, and understanding the implications is crucial.
The Mpox virus is transmitted through close contact with infected individuals, animals, or contaminated materials. Symptoms typically include fever, rash, swollen lymph nodes, and respiratory distress in severe cases. However, new strains, like the one recently discovered in China, may present unique characteristics.
The New Strain Identified in China
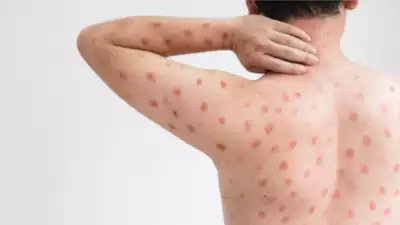
Chinese researchers have identified a novel strain of the Mpox virus that warrants urgent attention. Preliminary findings suggest this strain exhibits genetic mutations that could influence its transmissibility and pathogenicity. These mutations raise concerns about potential increased human-to-human transmission and the effectiveness of existing treatments and vaccines.
Key Characteristics of the New Strain:
- Genetic Variations: Mutations in the viral genome that may alter its replication efficiency and immune evasion strategies.
- Symptoms: Early reports indicate possible deviations in symptom presentation, including prolonged fever phases and atypical rash patterns.
- Transmission Dynamics: Initial investigations suggest a higher reproductive number (R0) compared to previous strains.
Possible Origins and Spread
The origins of this new strain remain under investigation. Experts suspect zoonotic spillover events in regions where human activity intersects with wildlife habitats, possibly exacerbated by climate change and urbanization. The strain’s detection in densely populated areas underscores the need for vigilant monitoring of community transmission.
Implications for Public Health
The emergence of a new Mpox strain poses significant challenges to global health systems. Key concerns include:
- Diagnostics: Existing tests may require updates to identify the new strain accurately.
- Vaccination: The efficacy of current vaccines, developed against previous Mpox strains, needs re-evaluation.
- Treatment Protocols: Antiviral treatments may require modifications to address potential resistance mechanisms.
Efforts must focus on enhancing surveillance, accelerating vaccine development, and fostering international collaboration to mitigate the spread. Know more: https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2025-01-09/china-disease-control-agency-detects-cluster-of-new-mpox-strain
Preventive Measures and Recommendations
Individual-Level Precautions:
- Practice good hygiene and avoid close contact with infected individuals.
- Report any unusual rashes or symptoms to healthcare providers promptly.
- Limit interactions with wildlife in regions reporting outbreaks.



 By
By









 By
By







